What do shares mean?
A share signifies part-ownership in a firm. When someone buys a share in a firm, they now own a part of that company. Over time, if the firm works well, the share value improves and the person who has shares in the company will reap the benefits—through profits in the form of dividends.
Trading refers to shares being listed, after which investors can buy and sell them. This describes how the share market works. It’s crucial to remember that the price of these shares can change every day because of changes in the market, demand and supply, or even how well the firm is doing.
How does a firm issue shares?
There is a fairly clear step-by-step method for a firm to issue shares:
- Draughting a Prospectus: The first step for the company is to write a prospectus, which is also called the Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP), and send it to the SEBI for assessment.
- SEBI clearance: Once this prospectus is presented to the SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India), if they are satisfied, they send it along for clearance.
- Apply to Stock Exchanges: After getting the green light, the company starts applying to stock exchanges like BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange) or NSE (NationalWhy does a company issue shares?
- The various reasons a company issues shares are as follows:
- Funding Growth: Companies release shares to fund expansion strategies, new projects, and new research and development without being weighed down by debt.
- Debt Settlement: Issuance of shares can relieve a company from the burden of debt liabilities because it raises funds from shareholders instead of loans that result in reduced interest costs.
- Improved Public Profile: It increases brand visibility by attracting potential customers, investors, and partners where once the company goes public through share issuance.
- Liquidity for Founders and Early Investors: It provides liquidity to the founders or early investors by giving them a partial exit while retaining ownership and gaining liquidity.
- Talent Attraction with Equity: Share issuance as compensation to employees attracts and retains talent because employee interest is tied to the company’sTypes of shares
The various kinds of stocks represent units of ownership in a company and can be categorized into several categories: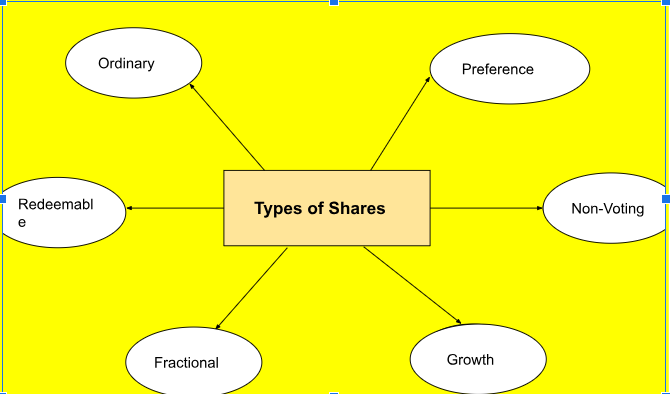
Ordinary Shares: Holders of these typically have voting rights and may receivewhich are paid out from the company’s profits. These types of shares are the most typical. - Preference Shares: Among the different types of shares, preference shareholders have a higher claim on assets and earnings. They usually receive fixed dividends before any dividends are paid to ordinary shareholders but typically do not have voting rights.
- Redeemable Shares: These types of shares can be bought back by the company at a predetermined price after a certain period.
- Non-voting Shares: These types of shares do not provide the shareholder with voting rights in company decisions but may still offer dividends.
- Fractional Shares: These represent a portion of a whole share, allowing investors to buy less than one full share, making investing more accessible.
- Growth Shares: These are shares in companies expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to their industry or the overall market.Features of equity shares
- Equity shareholders own a part of the business and have voting rights over crucial decisions made within it.
- Shareholders may receive dividends, which will be subject to the profits earned by the company and the dividend policy in place.
- Equity holders claim what’s left after all the debts and liabilities of the business are settled during liquidation.
- Equity shares are readily tradable on the stock exchange, thereby ensuring liquidation for the shareholder.
- Share prices may appreciate, and shareholders can receive potential capital gains.